Spike - Investigate running Dev container and code base in CodeSpaces
Spike: 01
Title: Investigate running Dev container and code base in CodeSpaces
Author: Brian Caldera, hcaldera@deakin.edu.au

Goals / Deliverables
Creating a cloud-based development environment using GitHub Codespaces to run Ontrack is a valuable initiative to streamline the setup process for students struggling with local development environments. To explore this, here’s a step-by-step guide on setting up Ontrack in a Codespace.
Codespaces offer a flexible, cloud-based development environment but might have limitations depending on the specific requirements of the application. Testing and validation are crucial to ensure it meets the needs of running Ontrack effectively.
Technologies, Tools, and Resources used
- Internet Browser; Google Chroame, FireFox, Safari
- GitHub Account
- GitHub Codespaces
- Docker
- Docker-in-Docker
- GitHub Repository: thoth-tech/dotfire-deploy, thoth-tech/doubtfire-web and thoth-tech/doubtfire-api
- Text Editor: VsCode
- Terminal: zsh
Tasks undertaken
-
Creating a Codespace
- Sign in to GitHub and navigate to the repository containing Ontrack. (Make sure you fork the repository first from thoth-tech/dotfire-deploy, thoth-tech/doubtfire-web and thoth-tech/doubtfire-api)
- Click on the “Code” button and select “Open with Codespaces” or navigate to “Code” > “New Codespace.”
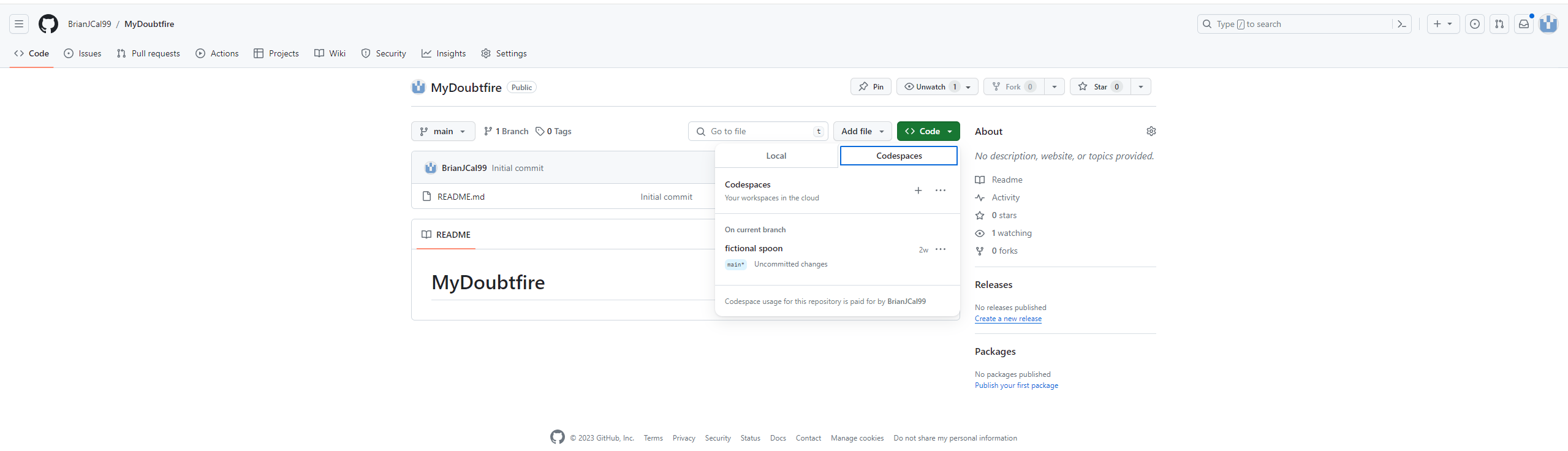
-
Install Docker-in-Docker in Codespace
- Confirm that Docker is installed and running in the Codespace by running the following command in the terminal: wihch docker
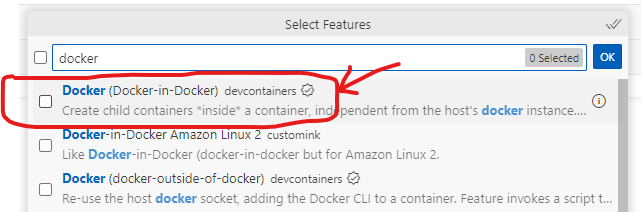
-
Configuring Codespace for Ontrack:
- Codespaces use a configuration file called .devcontainer to define the development environment. Create a .devcontainer folder in the root of the Ontrack repository if it doesn’t exist. (Replace this folder with the existing .devcontainer folder in the repository)
-
Running Ontrack in Codespace:
- Codespaces will use the defined configuration to create a containerized environment. It will automatically install dependencies, clone the repository, and set up Ontrack based on the configuration provided.
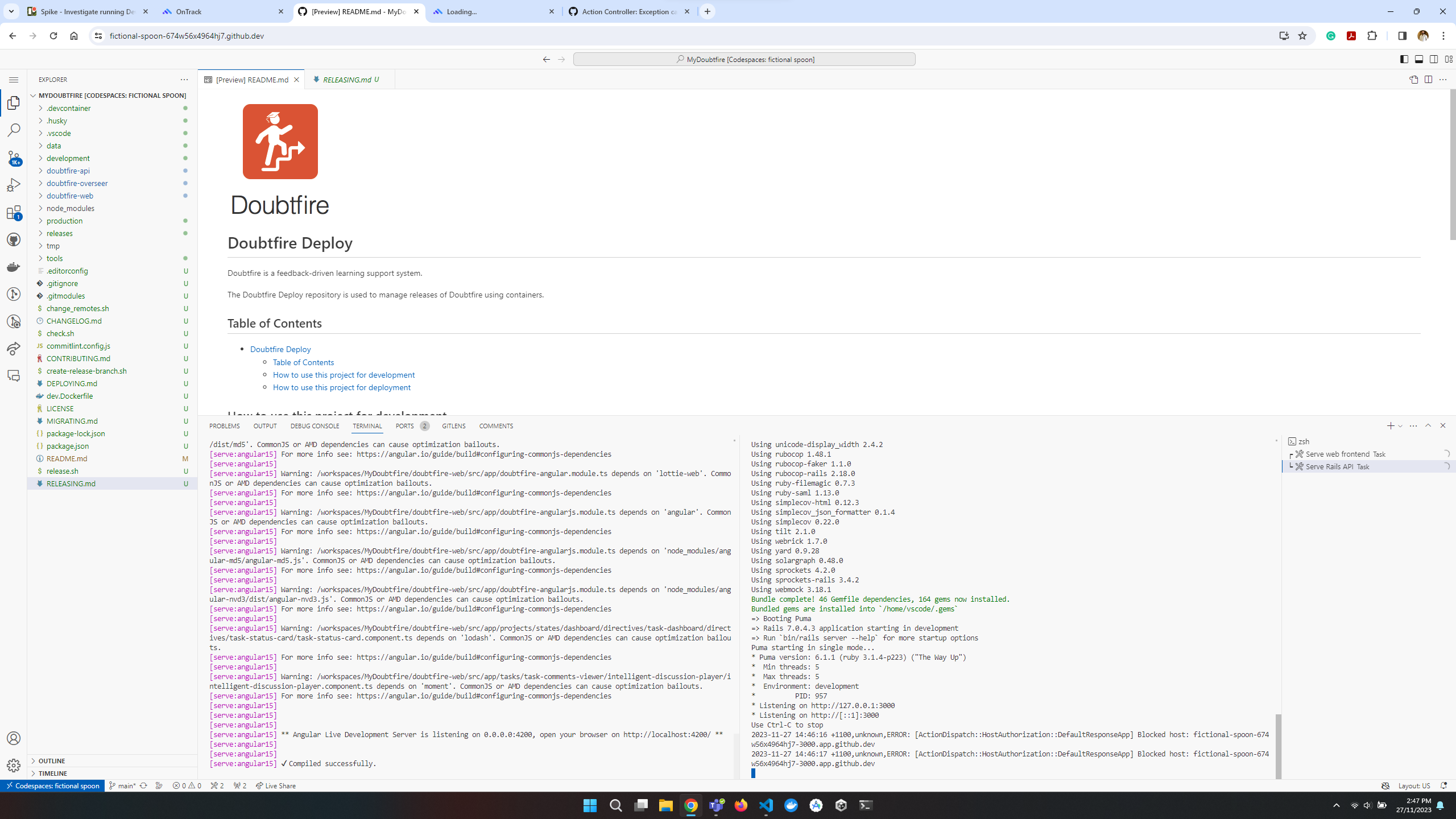
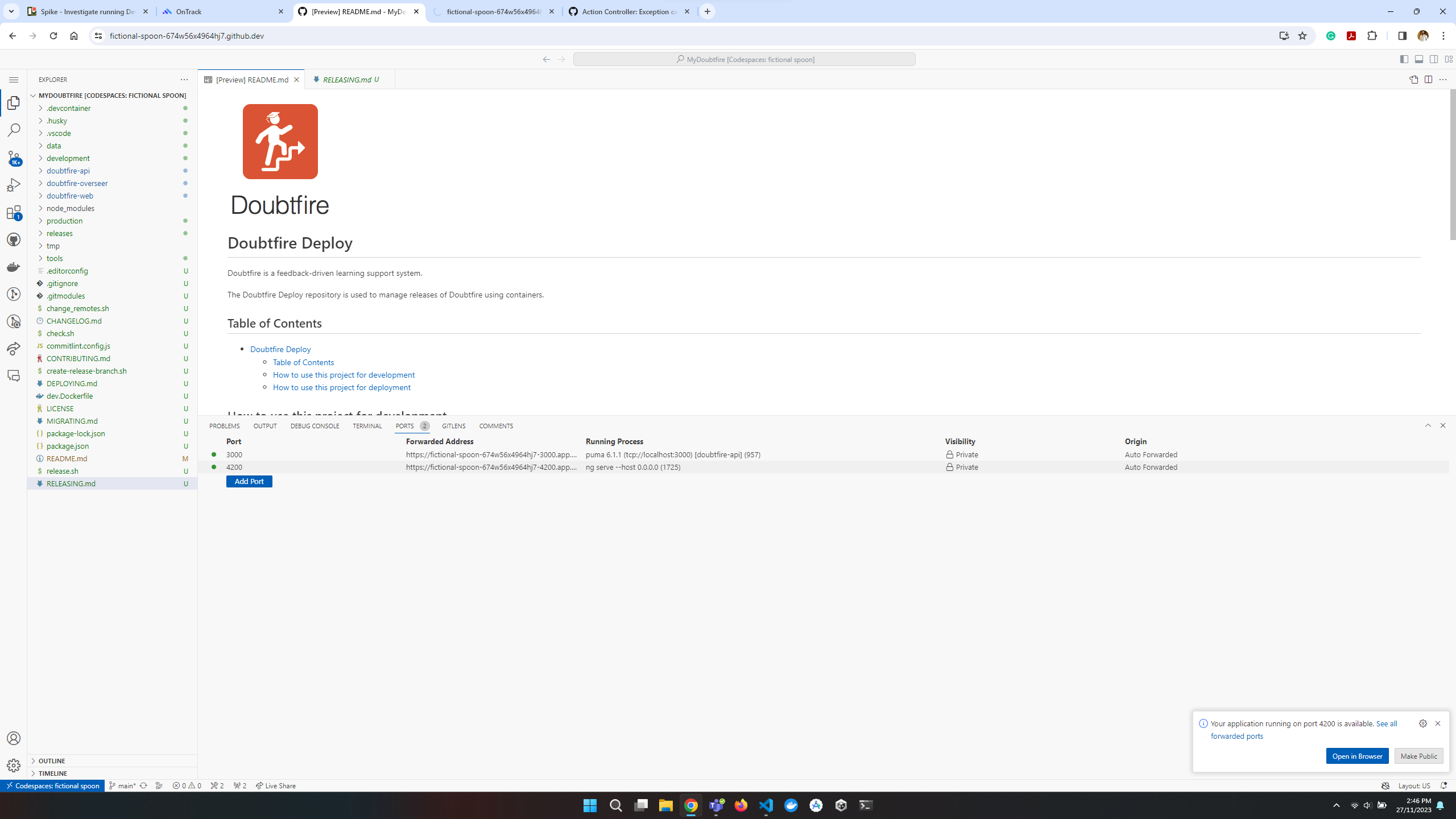
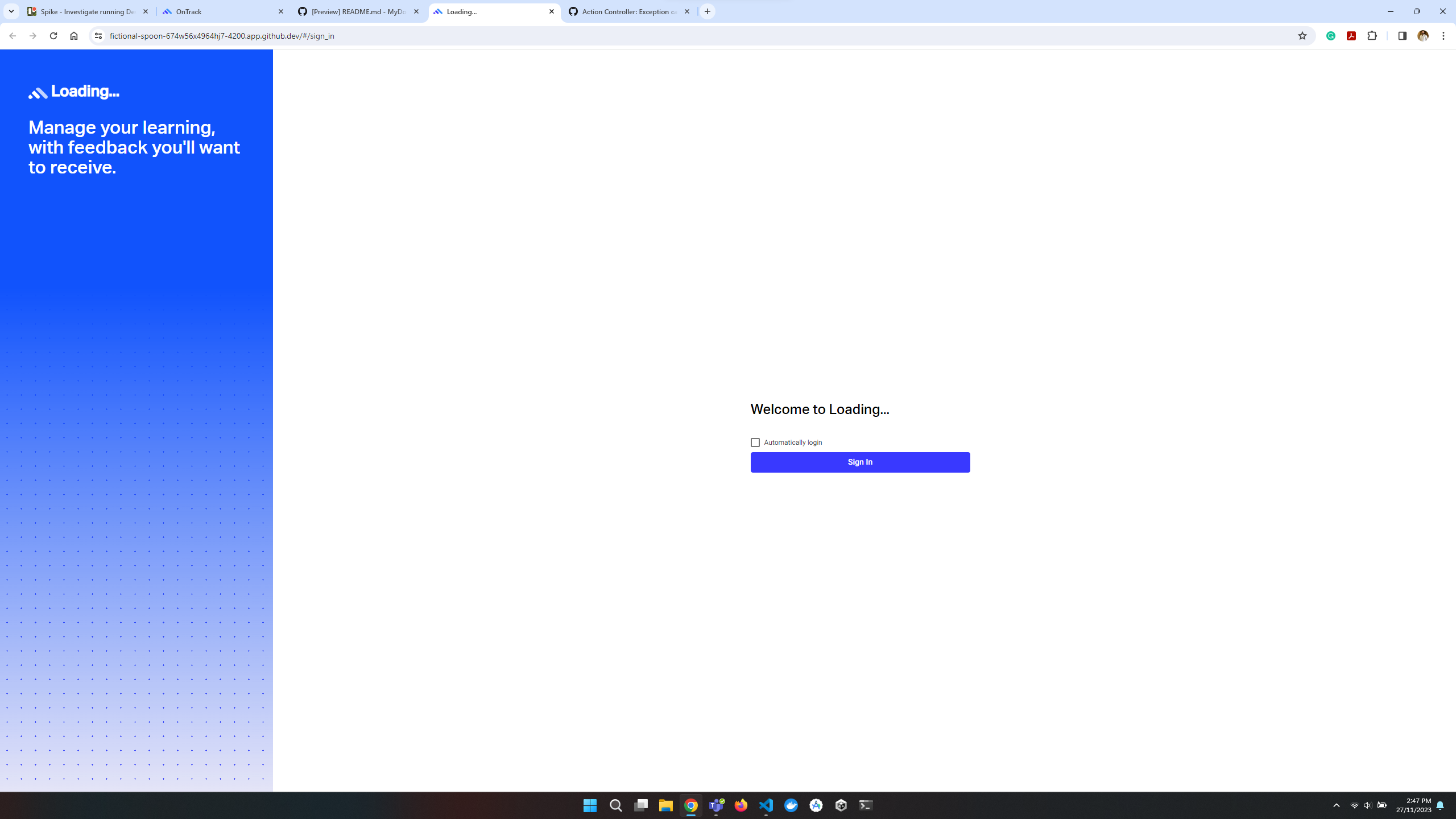
What we found out
The front-end seemed to run fine, but the back-end was not working as expected. The back-end server was not running, and the database was not connected. The following error was displayed in the terminal:
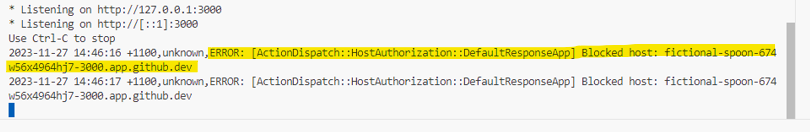
ERROR: ActionDispatch::HostAuthorization::DefaultResponseApp Blocked host: <github codespace host name>

Open issues/risks
Typically this error occurs when the Rails application is configured to allow requests only from specific hosts for security reasons. When attempting to access the application from an unauthorized host (in this case, the Codespace), this error is triggered.
To resolve this issue when running a Rails application in a Codespace, you can modify the configuration to allow requests from the Codespace host. Here are steps you can take:
- Step 1: Find the Codespace host name. (To determine the host that your Codespace is using, you can usually find it in the browser’s address bar when you access the application.)
- Step 2: Add the host name to the list of allowed hosts in the Rails application. (To do this, you can add the host name to the config.hosts array in the config/environments/development.rb file.)
- Step 3: Restart the Rails server. (To restart the Rails server, you can run the following command
in the terminal:
rails s)
Note:
Always ensure that the hosts allowed in the config.hosts array are trusted and secured. Adding a Codespace host should be done cautiously, especially in a production environment.
By adding the Codespace host to the allowed hosts in your Rails application’s configuration, you should be able to resolve the Blocked host error and access the application within the Codespace without issues.
Important:
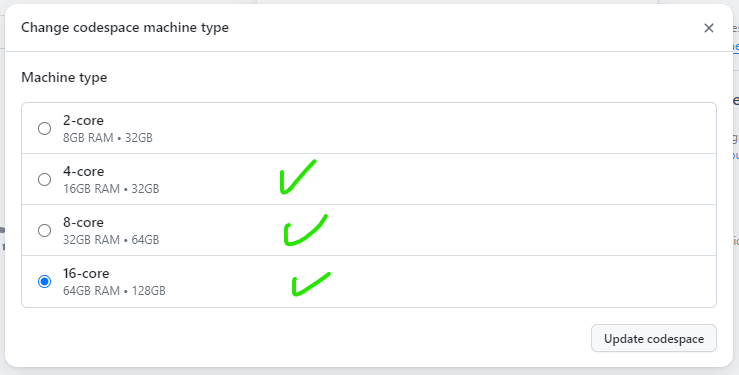
Ontrack demands substantial resources, specifically a minimum of a 4-core, 16GB RAM, 32GB virtual machine for smooth operation. This high resource demand could pose a potential issue with cost-effectiveness, as provisioning Codespaces meeting these specifications might lead to increased expenses, especially for extended use or multiple concurrent instances. Evaluating the cost implications alongside performance requirements is crucial before deciding to utilize GitHub Codespaces for running Ontrack’s development environment. Further optimization or alternative hosting solutions might need consideration to balance performance needs and cost efficiency effectively.
Recommendations
Despite encountering challenges related to the initial setup and resource requirements, this spike has significantly increased the team’s confidence in the feasibility of deploying Ontrack on GitHub Codespaces. While there were hurdles to overcome regarding security configurations and resource-intensive demands, the successful resolution of these issues demonstrates the adaptability and potential of utilizing Codespaces for development purposes.
It is recommended that the team proceed with caution and further exploration of deploying Ontrack on GitHub Codespaces. However, before full implementation, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should be conducted to assess the long-term financial implications of maintaining Codespaces meeting Ontrack’s resource demands. Additionally, ongoing optimizations and adjustments to streamline the development environment within Codespaces could enhance efficiency and mitigate potential cost concerns.
With careful consideration of costs, continuous optimization efforts, and confidence gained from this spike, the team can move forward confidently toward leveraging GitHub Codespaces for Ontrack’s development environment, recognizing its potential benefits for the development workflow.